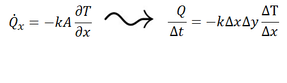Analysis Techniques |
JBL utilizes an array of techniques to deliver accurate, detailed results to clients |
Computational Fluid Dynamics
JBL has expertise in a wide range of fluids problems, but what is Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)?
Fluids are materials that deform continuously when shear is applied. Gasses, liquids, slurries, and fine particles are common examples of fluids. Since these materials cannot withstand shearing, they tend to be in motion in many industrial applications. CFD is a way to model the pressure, velocity, and temperature fields within fluids using systems of analytical equations and constitutive models (like equations of state and viscosity models).
|
Geometry for the solid objects which bound the fluid are drawn using a computer aided drafting package or other specialized software
|
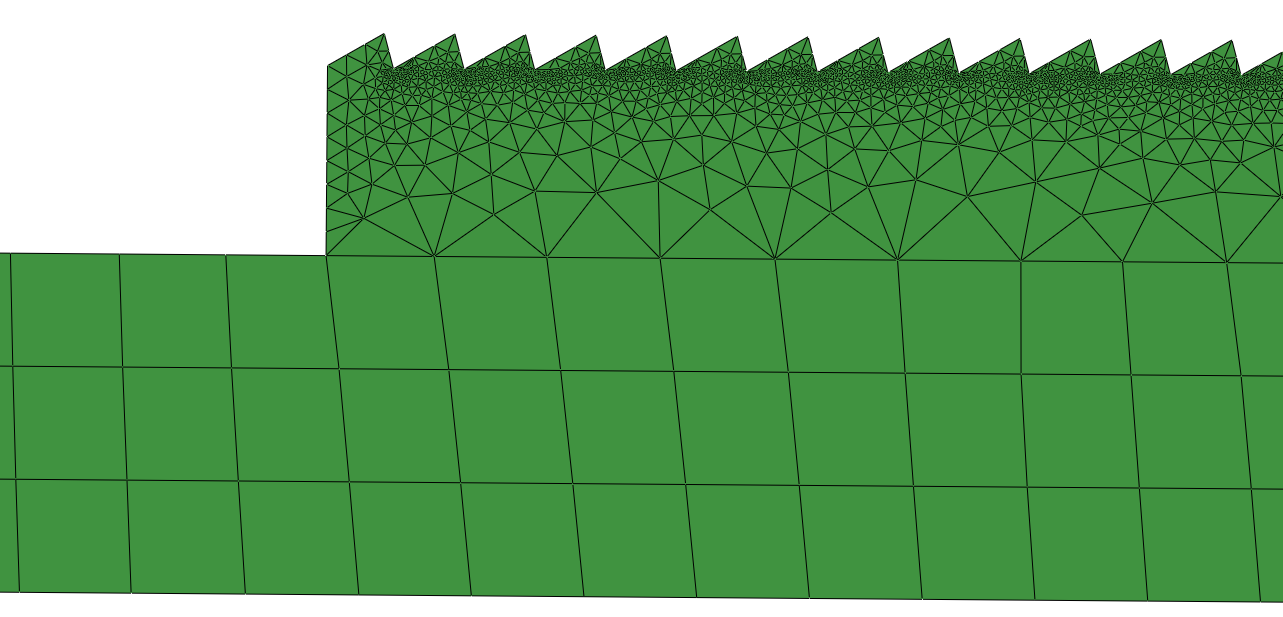
The geometry is "meshed" or discretized into small volumes and surfaces, creating a network of nodes (points) and elements (areas in 2D; volumes in 3D)
|
Equations of state link together fundamental properties of a fluid. Viscous models describe how stress is propagated through the medium. Both are critical in making a realistic CFD case.
|
|
The governing differential equations describing the physics of the problem are expressed as algebraic approximations within the CFD software package.
|
The software's pre-processor develops matrix representations of the algebraic governing and constitutive equations that are iteratively solved for all nodes in the model
|
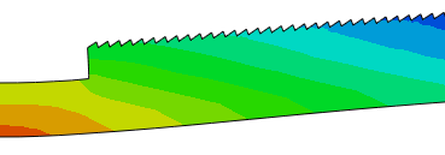
Once a converged solution is reached (meaning that the matrix equations have been solved within a specified tolerance), a post-processor can be used to visualize the relevant fields within the geometry
|
Proudly powered by Weebly